Waterfall Recurring Revenue Report for a Technology Company
What is
a
Waterfall Recurring Revenue Report
? Waterfall reports for recurring revenues are considered subscription analysis tools and are often used by sales executives and budgeting managers to track current and future recurring revenues. Some of the key functionality in this type of report is that it displays actual recurring revenues by month and shows how a sales amount has been spread into future months in the current calendar year. In the columns on the right, the running year-to-date amount is automatically calculated and compared to the budget, with a variance column on the far right (not visible in the screenshot below). You find an example of this type of report below.
Purpose of
Recurring Revenue Waterfall Reports Tech companies use Recurring Revenue Waterfall Reports to easily track recognized and upcoming subscription revenue amounts from existing contracts. When used as part of good business practices in a sales or FP&A department, a company can improve its revenue visibility and cash flow planning as well as reduce the chances that sales execs and planners forecast revenues without full understanding of revenues booked into future months.
Recurring Revenue Waterfall Report
Example Here is an example of Recurring Revenue Waterfall Report. [caption id="" align="alignnone" width="2560"]
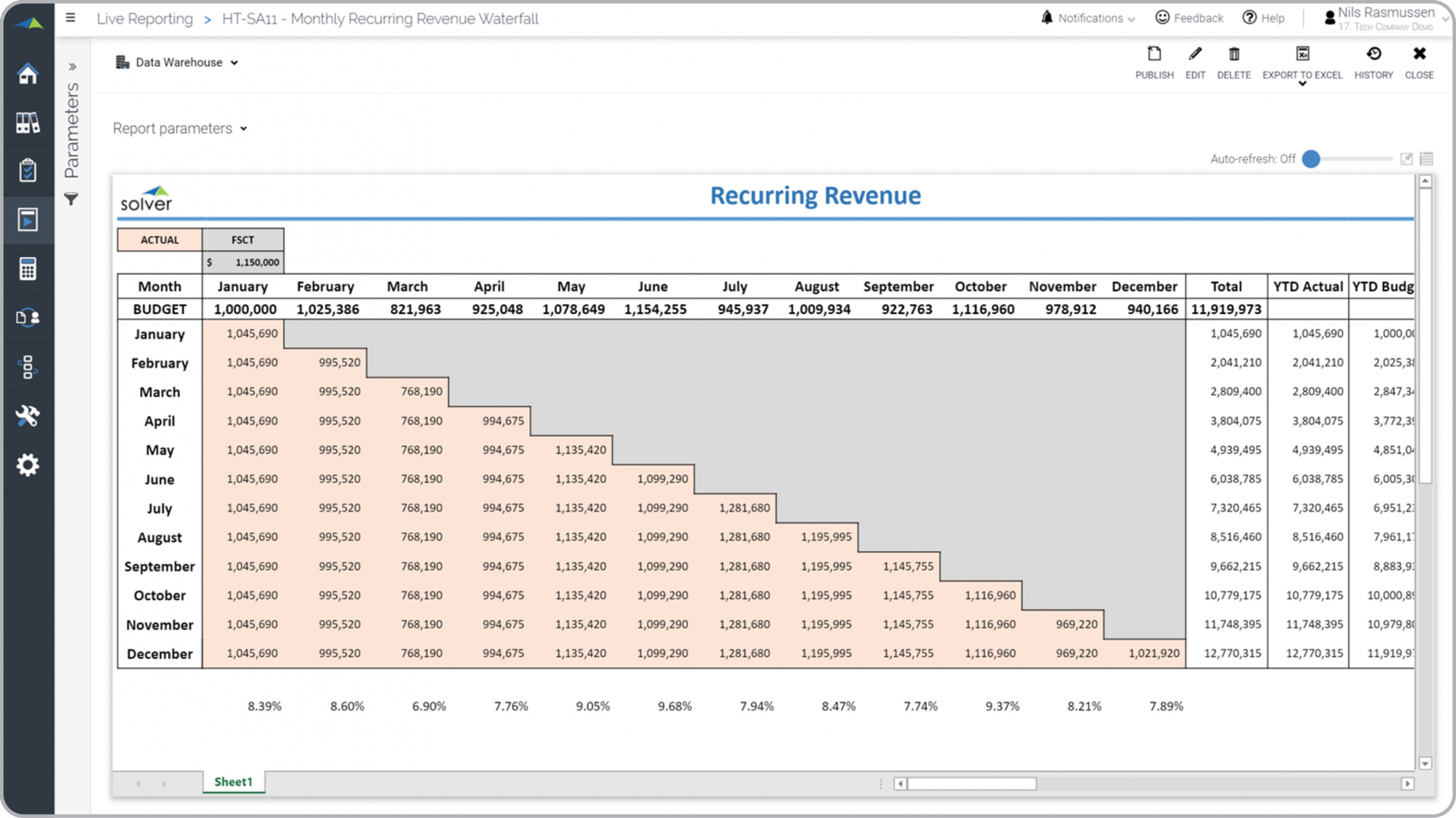 Example of Waterfall Recurring Revenue Report for a Technology Company[/caption] You can find hundreds of additional examples
here
Who Uses This Type of
Report
? The typical users of this type of report are: Sales executives, budget managers.
Other
Report
s Often Used in Conjunction with
Recurring Revenue Waterfall Reports Progressive sales or FP&A Departments sometimes use several different Recurring Revenue Waterfall Reports, along with sales reports, sales dashboards, recurring revenue dashboards, sales and revenue forecasts and other management and control tools.
Where Does the Data for Analysis Originate From? The Actual (historical transactions) data typically comes from enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems like: Microsoft Dynamics 365 (D365) Finance, Microsoft Dynamics 365 Business Central (D365 BC), Microsoft Dynamics AX, Microsoft Dynamics NAV, Microsoft Dynamics GP, Microsoft Dynamics SL, Sage Intacct, Sage 100, Sage 300, Sage 500, Sage X3, SAP Business One, SAP ByDesign, Acumatica, Netsuite and others. In analyses where budgets or forecasts are used, the planning data most often originates from in-house Excel spreadsheet models or from professional corporate performance management (CPM/EPM) solutions.
What Tools are Typically used for Reporting, Planning and Dashboards? Examples of business software used with the data and ERPs mentioned above are:
Example of Waterfall Recurring Revenue Report for a Technology Company[/caption] You can find hundreds of additional examples
here
Who Uses This Type of
Report
? The typical users of this type of report are: Sales executives, budget managers.
Other
Report
s Often Used in Conjunction with
Recurring Revenue Waterfall Reports Progressive sales or FP&A Departments sometimes use several different Recurring Revenue Waterfall Reports, along with sales reports, sales dashboards, recurring revenue dashboards, sales and revenue forecasts and other management and control tools.
Where Does the Data for Analysis Originate From? The Actual (historical transactions) data typically comes from enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems like: Microsoft Dynamics 365 (D365) Finance, Microsoft Dynamics 365 Business Central (D365 BC), Microsoft Dynamics AX, Microsoft Dynamics NAV, Microsoft Dynamics GP, Microsoft Dynamics SL, Sage Intacct, Sage 100, Sage 300, Sage 500, Sage X3, SAP Business One, SAP ByDesign, Acumatica, Netsuite and others. In analyses where budgets or forecasts are used, the planning data most often originates from in-house Excel spreadsheet models or from professional corporate performance management (CPM/EPM) solutions.
What Tools are Typically used for Reporting, Planning and Dashboards? Examples of business software used with the data and ERPs mentioned above are:
- Native ERP report writers and query tools
- Spreadsheets (for example Microsoft Excel)
- Corporate Performance Management (CPM) tools (for example Solver)
- Dashboards (for example Microsoft Power BI and Tableau)
Corporate Performance Management (CPM) Cloud Solutions and More Examples
October 13, 2020
TAGS:
Reporting,
Solver,
report writer,
Microsoft,
consolidation,
template,
practice,
Acumatica,
Netsuite,
Finance,
GP,
Business Central,
excel,
ARR,
ax,
subscription sales,
forecast,
Budget,
forecasting,
budgeting,
Cloud,
Software,
recurring revenue,
Tableau,
SAP,
example,
best,
Sage,
BC,
D365,
NAV,
Intacct,
CPM,
report,
mrr,
SL,
Management,
dynamics,
Power BI

