High-Impact Ideas
Recent Posts
Consolidated Accounts Receivable Report
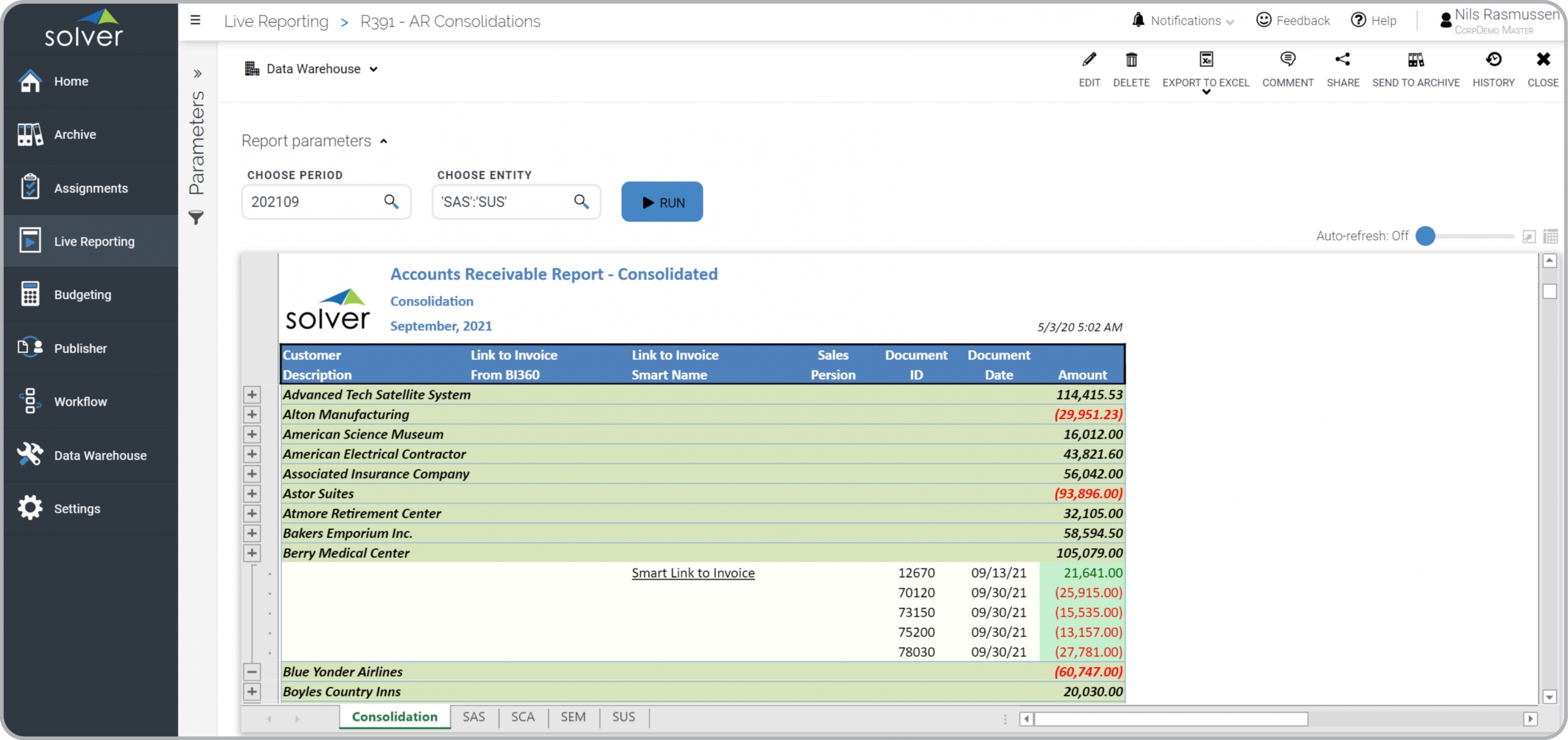 Consolidated Accounts Receivable (AR) Report Example[/caption] You can find hundreds of additional examples
here.
Who Uses This Type of
Report
? The typical users of this type of report are: Group Controllers and Accountants.
Other
Report
s Often Used in Conjunction with
Consolidated Accounts Receivable Reports Progressive Finance & Accounting Departments sometimes use several different Consolidated Accounts Receivable Reports, along with AR Aging reports, consolidated accounts payable reports, sales reports and other management and control tools.
Where Does the Data for Analysis Originate From? The Actual (historical transactions) data typically comes from enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems like: Microsoft Dynamics 365 (D365) Finance, Microsoft Dynamics 365 Business Central (D365 BC), Microsoft Dynamics AX, Microsoft Dynamics NAV, Microsoft Dynamics GP, Microsoft Dynamics SL, Sage Intacct, Sage 100, Sage 300, Sage 500, Sage X3, SAP Business One, SAP ByDesign, Acumatica, Netsuite and others. In analyses where budgets or forecasts are used, the planning data most often originates from in-house Excel spreadsheet models or from professional corporate performance management (CPM/EPM) solutions.
What Tools are Typically used for Reporting, Planning and Dashboards? Examples of business software used with the data and ERPs mentioned above are:
Consolidated Accounts Receivable (AR) Report Example[/caption] You can find hundreds of additional examples
here.
Who Uses This Type of
Report
? The typical users of this type of report are: Group Controllers and Accountants.
Other
Report
s Often Used in Conjunction with
Consolidated Accounts Receivable Reports Progressive Finance & Accounting Departments sometimes use several different Consolidated Accounts Receivable Reports, along with AR Aging reports, consolidated accounts payable reports, sales reports and other management and control tools.
Where Does the Data for Analysis Originate From? The Actual (historical transactions) data typically comes from enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems like: Microsoft Dynamics 365 (D365) Finance, Microsoft Dynamics 365 Business Central (D365 BC), Microsoft Dynamics AX, Microsoft Dynamics NAV, Microsoft Dynamics GP, Microsoft Dynamics SL, Sage Intacct, Sage 100, Sage 300, Sage 500, Sage X3, SAP Business One, SAP ByDesign, Acumatica, Netsuite and others. In analyses where budgets or forecasts are used, the planning data most often originates from in-house Excel spreadsheet models or from professional corporate performance management (CPM/EPM) solutions.
What Tools are Typically used for Reporting, Planning and Dashboards? Examples of business software used with the data and ERPs mentioned above are:
- Native ERP report writers and query tools
- Spreadsheets (for example Microsoft Excel)
- Corporate Performance Management (CPM) tools (for example Solver)
- Dashboards (for example Microsoft Power BI and Tableau)
- View 100’s of reporting, consolidations, planning, budgeting, forecasting and dashboard examples here
- Discover how the Solver CPM solution delivers financial and operational reporting
- Discover how the Solver CPM solution delivers planning, budgeting and forecasting
- Watch demo videos of reporting, planning and dashboards
TAGS: Reporting, Solver, report writer, Microsoft, consolidation, aging, template, practice, Acumatica, customer, Netsuite, Finance, GP, Business Central, AR, excel, ax, budgeting, Cloud, Software, receivables, consolidated, Tableau, SAP, example, best, Sage, BC, D365, NAV, Intacct, CPM, report, SL, Management, dynamics, Power BI
Global Headquarters
Solver Suite
Core Subscription
Company and Resources
© Copyright 2024, Solver All rights reserved.LegalPrivacy
QuickStart and Template Marketplace Overview (2 min) |QuickStart and Template Marketplace Setup (10 min)
Global Headquarters
Solver Suite
Core Subscription
Company and Resources
© Copyright 2024, Solver All rights reserved.LegalPrivacy
QuickStart and Template Marketplace Overview (2 min) |QuickStart and Template Marketplace Setup (10 min)
Global Headquarters
Solver Suite
Core Subscription
Company and Resources
© Copyright 2024, Solver All rights reserved.LegalPrivacy
QuickStart and Template Marketplace Overview (2 min) |QuickStart and Template Marketplace Setup (10 min)
Global Headquarters
Solver Suite
Core Subscription
Company and Resources
© Copyright 2024, Solver All rights reserved.LegalPrivacy
QuickStart and Template Marketplace Overview (2 min) |QuickStart and Template Marketplace Setup (10 min)
